Most recently, the research group led by Prof. XIONG Yujie made new progress on the design of hybrid photocatalysts for water splitting. In this work, they for the first time achieved to synergize two effects – the charge transfer driven by Schottky barrier and the intrinsic charge spatial separation in semiconductor by designing the surface facets of semiconductor in a semiconductor-metal hybrid structure, enabling significantly improved water splitting performance. Teamed up with Prof. JIANG Jun and Prof. ZHANG Qun, the researchers performed the studies by integrating controlled synthesis with theoretical simulations and advanced characterizations, and discovered the importance of surface work function in the synergetic use of the two effects. This progress has been published in
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. online (
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201310635).
In the photocatalysis, the migration of holes has notably lower rate than that of photoexcited electrons, limiting the total efficiency of reactions. The researchers proposed a strategy to facilitate the migration of holes in semiconductor by taking advantage of the Schottky barrier between p-type semiconductor and metal. They found that high work function serves as an important selection rule for building such desirable Schottky junction between semiconductor surface facets and metal. On the other hand, they also demonstrate that the intrinsic charge spatial distribution has to be taken into account when selecting the facets, as it results in accumulation of photoexcited electrons and holes on certain semiconductor facets. Importantly, the facets turn out to have high work function, the same characteristic required for the formation of Schottky junction in a p-type semiconductor-metal hybrid structure. As such, they have been able to define the rule for hybrid photocatalysts design: the semiconductor crystals in the hybrid design may better be enclosed by single facets with high work function, so as to synergize the two effects (Schottky barrier versus charge spatial separation). It is anticipated that this work casts new light on photocatalysts design in consideration of facet effect.
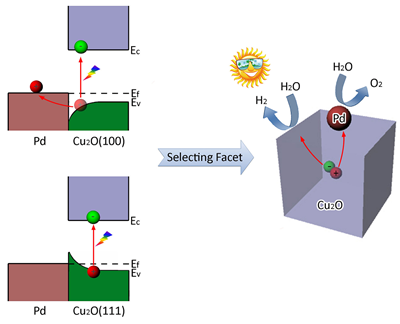
Schematic illustrating the importance of facet selection to Cu2O-Pd hybrid system in water splitting
This work was supported by 973 Program, NSFC, Recruitment Program of Global Experts, CAS Hundred Talent Program, and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
(HFNL)