—Chinese Scientists Demonstrated Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution Immune to Detector Attacks
Scientists from University of Science and Technology (USTC) led by Prof. PAN Jianwei and Prof. CHEN Tengyun, and from Tsinghua University (THU) led by Prof. MA Xiongfeng successfully demonstrated themeasurement-device-independent quantum key distribution by developing up-conversion single-photon detectors with high efficiency and low noise. The new quantum encryption method provides the ultimate security against hackers in real-world cryptography applications, which greatly improve the security of quantum encryption systems.
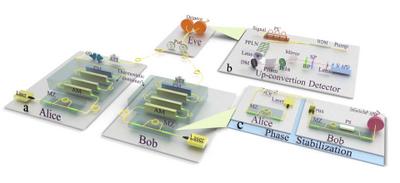
Fig: The up-conversion single-photon detectors.
Quantum key distribution is proven to offer unconditional security in communication between two remote users with ideal source and detection. Unfortunately, ideal devices never exist in practice and device imperfections have become the targets of various attacks. In the last few years, hackers have exploited security loopholes to crack some of the most sophisticated quantum encryption systems. How can the loopholes with defects of the photodetectors used at the receive end be removed? Fortunately, the measurement-device-independent quantum-key-distribution protocol developed by Pan’s groups provides solution to the problem.
By developing up-conversion single-photon detectors with high efficiency and low noise, Pan and his colleagues, for the first time on world, demonstrated the measurement-device-independent quantum-key-distribution protocol, which is immune to all hacking strategies on detection. Meanwhile, they employed the decoy-state method to defend attacks on a nonideal source. By assuming a trusted source scenario, their practical system, which generates more than a 25 kbit secure key over a 50 km fiber link, serves as a stepping stone in the quest for unconditionally secure communications with realistic devices.
(TIAN Lin, USTC News Center)