A team led by Prof. YAO Hongbin from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) developed a high efficiency, high brightness warm white light-emitting diode (LED) based on copper-iodide cluster hybrids. Their work was published in Nature Photonics on December 19th.
Solution-processed LED are considered to be the technology for realizing the next generation of large-area solid-state lighting due to their simple manufacturing process and high operability. At present, solution-processed LED devices based on lead-halide perovskites, organic semiconductors materials, and colloidal core-shell quantum dots (QDs) have achieved high electroluminescence performance.
However, materials containing heavy metals such as lead-halide perovskites and CdSe QDs cause serious environmental issues, while LED devices based on organic light-emitting molecules, InP QDs and ZnSe QDs have high production cost due to their complex synthesis. Therefore, developing solution-processed LED based on low-cost, low-toxicity, easily scalable and highly efficient emitter is the key challenge for future solid-state lighting.
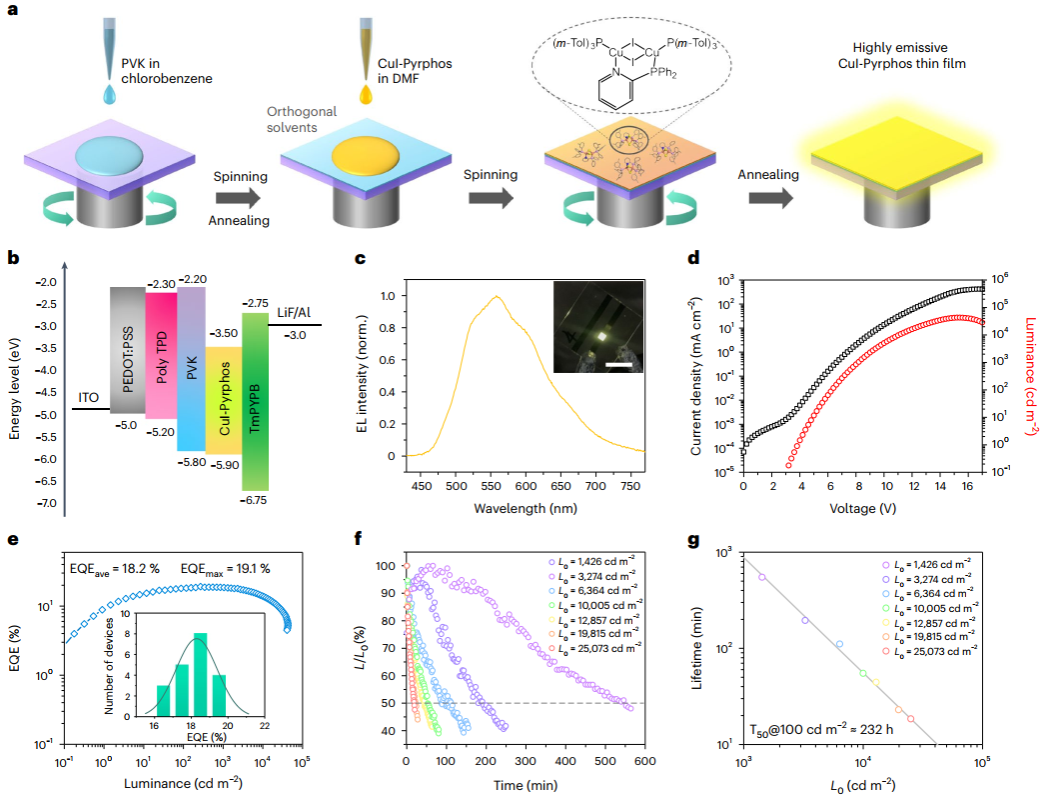
Fabrication process and characteristics of the solution-processed LED developed by the team. (Image by Prof. YAO’s team)
To tackle this challenge, the team first designed and prepared a copper-iodine-based hybrid cluster with a broad photoluminescence spectrum. By introducing nitrogen-phosphine chelating ligands and phosphine-containing solubilizing ligands, the team obtained copper-iodide hybrid clusters with both high luminescence efficiency and high solubility, which show a high solubility of more than 200 mg/mL and good structural stability in N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF), the cross-solvent used in LED production. The luminescent thin films fabricated by spin-coating in DMF exhibit a low surface roughness of 0.22 nm and a high photoluminescence quantum yield of more than 70%, which can be used as a luminescent layer to make low-cost warm-white LED devices through an orthogonal solvent route.
The resulting LED devices achieve a maximum external quantum efficiency of 19.1%, a brightness of more than 40,000 cd m-2, and an operational lifetime of more than 232 h (T50@100 cd m-2). Meanwhile, thanks to the good solubility and processability of the clusters, the team constructed a large-area solution-processed LED device with a working area of 36 cm2 through blade-coating, which exhibited warm white light emission with brightness close to 60,000 cd m-2. In addition, by modifying different electron-donating groups on the nitrogen heterocycles of the nitrogen-phosphine chelating ligands, the team developed a series of solution-processed color-tunable LED devices.
This work realized LED devices with high-efficiency and high-brightness based on copper-iodide hybrid cluster. The structural expandability and spectral tunability of the copper-iodide hybrid clusters make them promising for fabricating low-cost high-performance LED panels and solid-state lighting.
Paper link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-023-01340-8
(Written by LI Rui, edited by ZHANG Yihang, USTC News Center)